Phys24-001, Fall 2000 Exam 1
Name _________________________________ Seat Number ________ Sequence Number: 101
Honor Pledge and signature:
I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination. _____________________
Instructions:
This exam is closed book, closed notes. However, you may use a calculator.
Mark your answers to the multiple choice questions on a Scantron answer sheet.
If you do not find your answer, write your solution on these pages and mark option 5.
Equations and
conversion factors that may be useful:
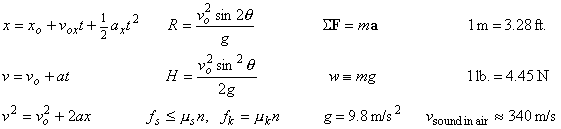
Knowledge Questions (2 points each)
1. If an equation is dimensionally correct, this means that the equation must be true. 1. True 2. False
2. Instantaneous velocity is a vector. 1. True 2. False
3. It is possible for a single isolated force to exist by itself . 1. True 2. False
4. Whenever an object is resting on a horizontal surface, the normal force pushing up on the object is equal to its weight. 1. True 2. False
5. What are the base units for a Newton?
1. kg×m2/s2 2. kg×m2/s 3. kg2×m/s2 4. kg×m/s2
Conceptual Questions (3 points each)
6. Why is it important to report quantitative results rounded to the appropriate number of significant figures?
1. It is misleading to state a greater precision than what is known
2. WebAssign allows a 1% default tolerance for numerical results
3. The number of significant figures should be consistent with the uncertainty of the result
4. All of the above
7. Without air resistance, an object dropped from a plane flying at constant velocity will:
1. Follow a parabolic trajectory (as viewed from the ground), but remain directly beneath the plane
2. Fall straight down in a vertical line (as viewed from the ground)
3. Lag behind the plane
4. Move ahead of the plane
8. A ball is thrown vertically upward with an initial speed of 20 m/s. When it momentarily stops at the top, its acceleration is:
1. Zero
2. 10 m/s
3. g
4. - g
9. Which of the following graphs matches the previous question:
10. A ball is thrown downward (not dropped) from the top of a tower. After being released, its downward acceleration will be (ignoring air resistance)
1. Greater than g.
2. Exactly g
3. Less than g
11. A person standing at the edge of a cliff throws one ball straight up and another ball straight down at the same initial speed. Neglecting air resistance, which ball will hit the ground with the greater speed?
1. The one initially thrown upward
2. The one initially thrown downward
3. Neither – they both will hit the ground at the same speed
4. There is not enough information to answer this question
12. You are pushing a wooden crate across a concrete floor at a constant speed, when you decide that it might be easier to push the crate if you turn it up on its end so that only half of the original surface area is in contact with the floor. The force required to push the crate in this new orientation (compared to before) is about:
1. Twice as great
2. Equally great
3. Half as great
4. One-fourth as great
13. Two cars are traveling at the same speed on a level road when their drivers see a red light and slam on the brakes to come to a screeching halt. Both cars are similar in design, but car A has twice the mass of car B. Which car stops first?
1. Car A
2. Car B
3. Both cars stop at the same time
4. More information is needed to answer this question
14. A big truck collides with a small car. Which experiences a greater force?
1. The truck
2. The car
3. Both experience the same force
4. Not enough information to determine
15. Two metal balls roll off a horizontal table with the same speed. Ball A has twice the mass of ball B. Which ball lands closer to the table?
1. Ball A
2. Ball B
3. Neither, they both travel the same horizontal distance
4. Not enough information to determine
Quantitative Questions (3 points each)
16. Your crazy California friend is planning a “Coast to Coast for Coats” fund-raiser in which she will raise money to buy coats for children by walking from Los Angeles to New York. She will be walking unassisted, except for a support vehicle with food, water, a bed, and medical supplies. About how long would you expect her walk-a-thon to last (assuming she is successful in her goal)?
1. Less than a month
2. Three to six months
3. Nearly a year
4. Over a year
17. Two friends pull you in different directions. One friend pulls with a force of 100 N to the east, and the other friend pulls with a force of 50 N to the north. What is the net force that causes you to accelerate?
1. 150 N at an angle of 63° east of north
2. 150 N at an angle of 63° north of east
3. 112 N at an angle of 27° east of north
4. 112 N at an angle of 27° north of east
18. In question #13 above, car A has a mass of 1500 kg. If its skid marks are 40 m long, what was its initial speed? (The coefficient of static friction between the tires and dry asphalt is about 1.0 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is about 0.8).
1. 20 m/s
2. 25 m/s
3. 28 m/s
4. There is not enough information to answer this question
19. You decide to estimate the height of the UNC bell tower by using your newly-acquired physics knowledge. You walk 100 paces (about 300 feet) from the base of the tower and observe that the top of the tower is about 30 degrees above horizontal. You conclude that the height of the tower is approximately
1. 150 ft.
2. 260 ft.
3. 173 m
4. 53 m
20. A firefighter, 50 m away from a 12-story burning building, directs a stream of water from a ground-level hose at an angle of 40° above horizontal. If the speed of the stream as it leaves the hose is 40 m/s, at what height does the water strike the building?
1. 24 m
2. 29 m
3. 34 m
4. 42 m
21. What is the maximum height of the water from the firefighter’s hose in the previous problem?
1. 24 m
2. 29 m
3. 34 m
4. 42 m
22. Two, 5-kg blocks of wood are stacked on top of each other as they rest on a ramp inclined at a 30° angle. The coefficient of static friction between the bottom block and the ramp is 0.5 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.3. What is the magnitude of the frictional force acting between the lower block and the ramp that keeps it from sliding?
1. 17 N
2. 24 N
3. 34 N
4. 46 N
23. If the top block is removed, will the bottom block slide down the ramp?
1. Yes
2. No
24. A woman in a stationary elevator weighs 600 N. As the elevator travels from the 1st to the 6th floor, it decreases its upward speed from 8 to 2 m/s in 3 s. What is the average force exerted by the elevator floor on the woman during this 3-second time interval?
1. 300 N
2. 480 N
3. 600 N
4. 720 N
25. A car traveling at a constant speed of 40 m/s passes a speed trap, at which point a waiting police car accelerates from rest at 4 m/s2. (Assume that the speeder does not slow down and the police car maintains a constant acceleration beginning the instant the speeder passes.) When the police car catches up with the speeder, which car will be traveling faster?
1. The police car
2. The speeding car
3. They both will be traveling at the same speed when they meet
4. We need to first calculate the time when they will meet
Optional survey
question (no credit):
26. Do you feel that this was a fair exam?
- Yes 2. No
Real-world Problem
(30 points)
Write your solution to the following problem using the
GOAL problem-solving template that is provided.
You are hiking in the mountains with some friends when you come across a deep chasm. One of your friends wonders if her 150-ft climbing rope is long enough to safely rappel down to the bottom. She decides to estimate the depth of the chasm by dropping a rock and timing its fall with her stopwatch. She starts timing as a medium-sized stone is dropped, and when she hears it hit the bottom, she stops the watch, which shows a time of 3.25 seconds. After carefully analyzing the situation, she decides to attempt the descent. Was this a wise decision?
|
Gather information: (10 points) What is known? What are you looking for? What assumptions or estimations must be
made? Predict a reasonable range of answers. Draw diagram with variables labeled. |
|
Organize your approach: (5
points) Classify the problem. Describe how you will
solve it.
|
|
Analyze the problem: (7 points) Identify and show relevant physics
equations. Solve for the unknown variable in terms of
the known variables. Substitute known values, calculate answer,
round appropriately. Account for real-world effects. |
|
Learn from your
efforts: (8 points) Does the answer agree with the prediction
in G step? Correct units? Does the solution account for all the
real-world factors that should be considered? If the problem were modified, how would the
result change? What else can be learned from this problem? |